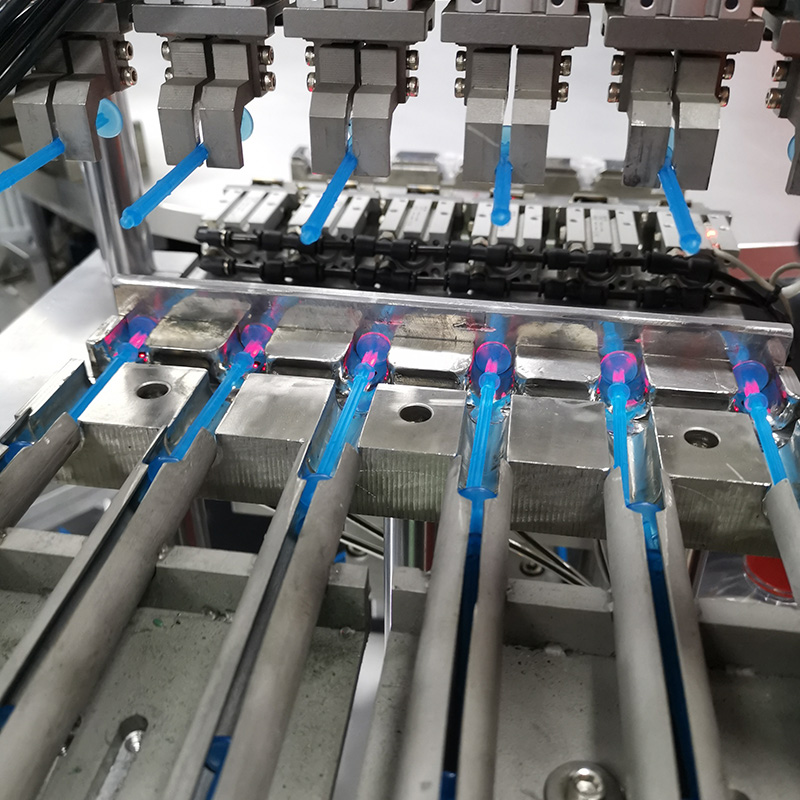
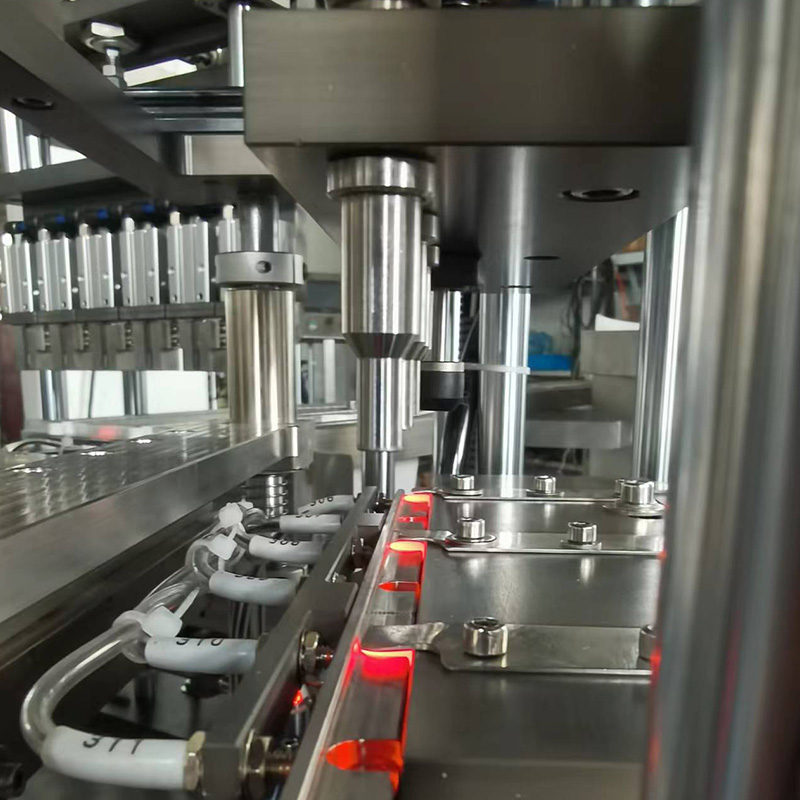
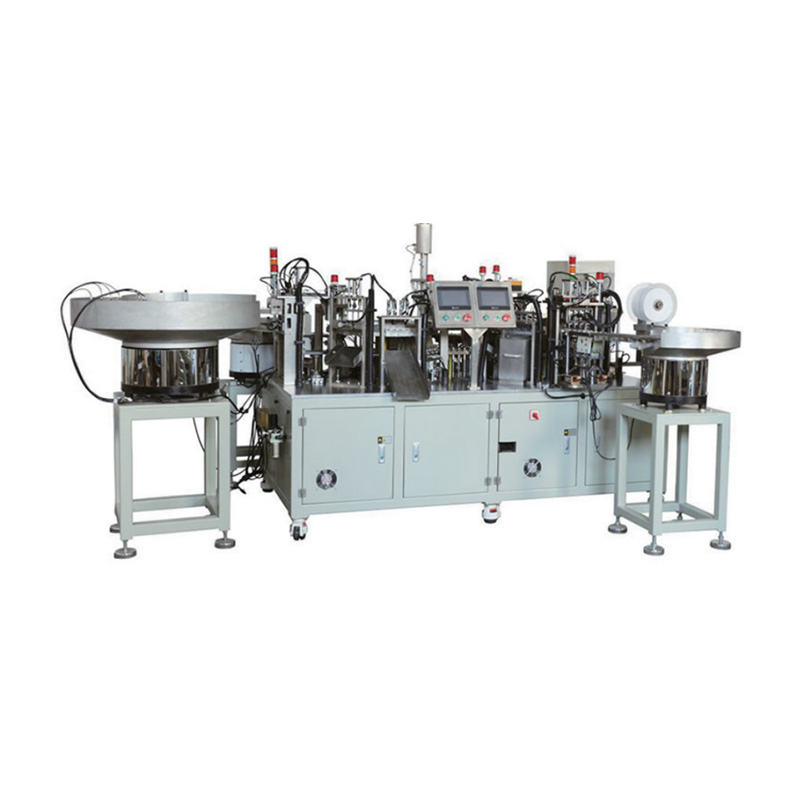
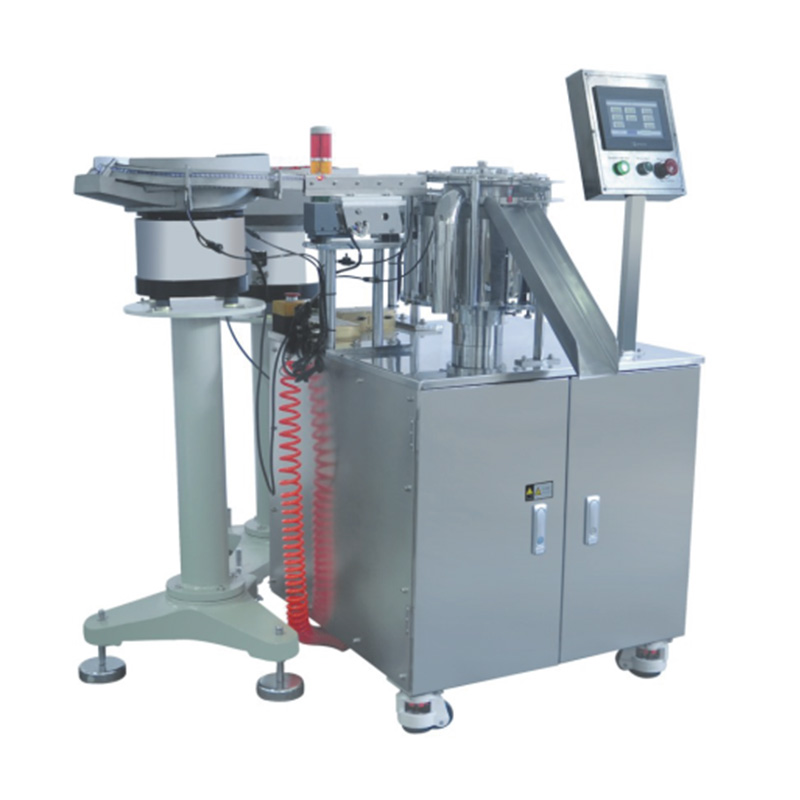
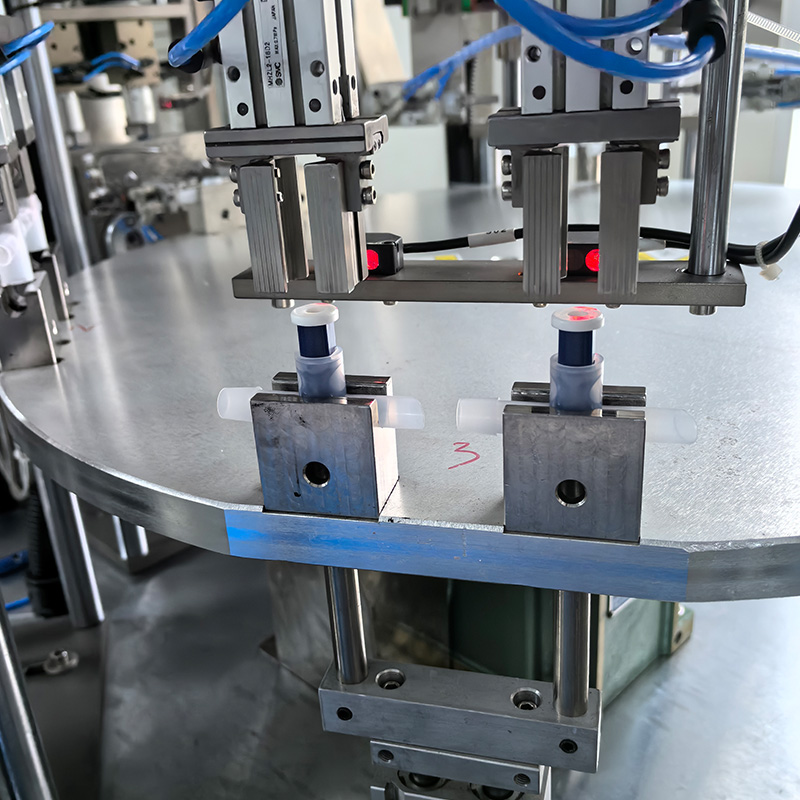
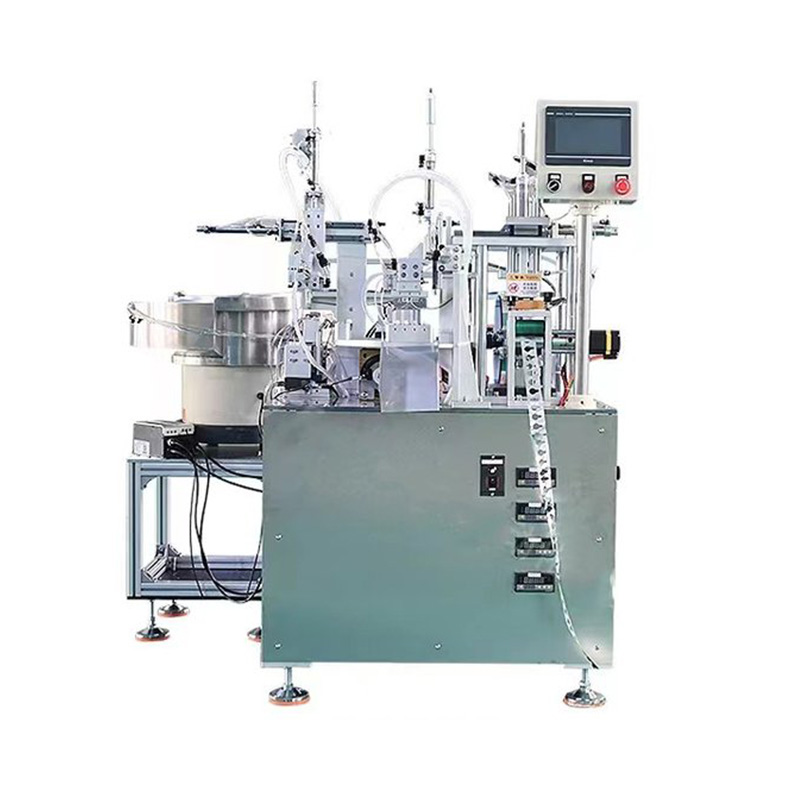
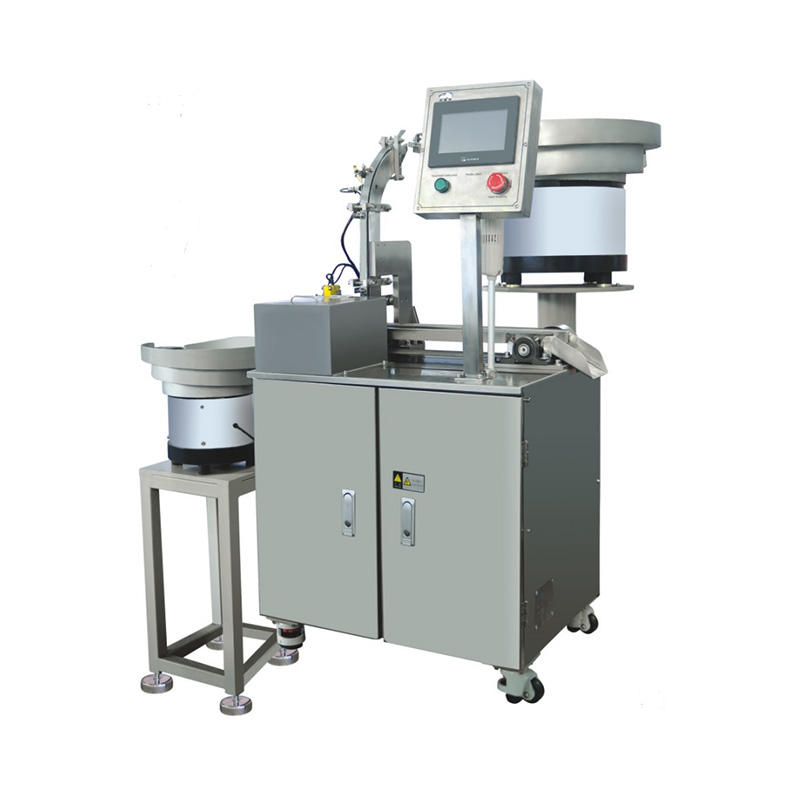
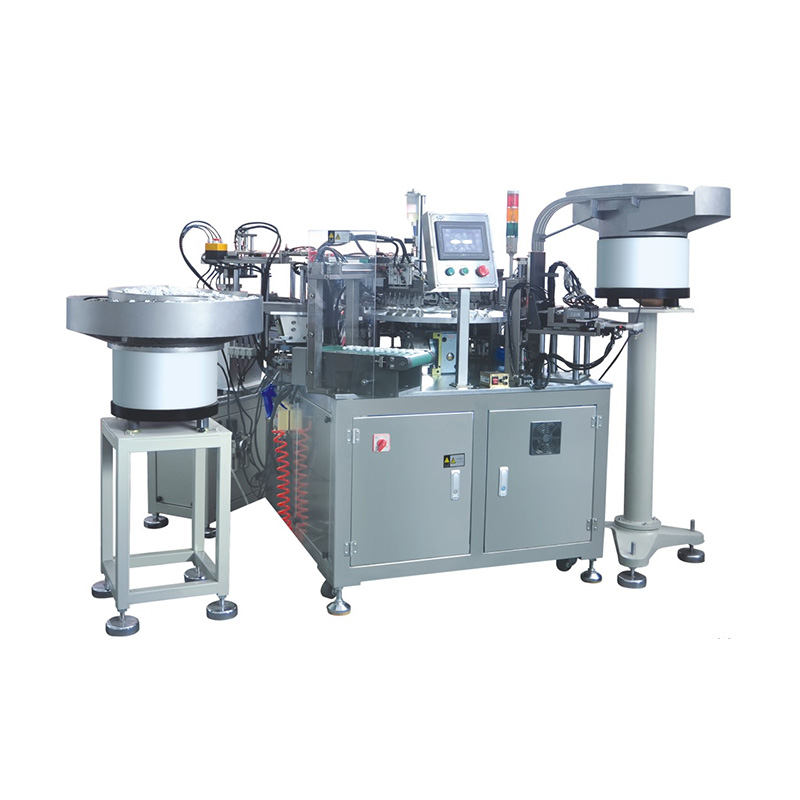
China Zhejiang Taizhou Ambe Trading Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer specializing in the production of automated equipment for medical devices. The company boasts a team of experts dedicated to the research and development of medical equipment. By adopting advanced technology, we have replaced traditional manual operations, achieving a level of sophistication on par with international counterparts. Guided by the principles of high technology, superior quality, and zero-defect service, we are committed to providing you with top-tier equipment and exceptional support.
The Structure and Components of a Three-Way Valve Mold
Upper Die and Lower Die:
The upper and lower dies work together to form the closed structure of the three-way valve.
The metal or plastic raw material is formed into a standard three-way valve shape through injection molding or compression molding.
Core Holder:
Secures the core component of the mold, ensuring it does not move or deform during processing.
Commonly used to secure the position of ball valves or other critical components.
Guide Block:
Used to locate and secure the relative position between the upper and lower dies, ensuring accurate molding.
Helps maintain mold stability during molding, reducing the risk of shifting or deformation.
Locate Pin:
Helps secure the mold during compression molding, preventing shifting or deformation.
Ensures a tight fit between the upper and lower dies, improving product sealing and stability.
Flow Channel Design:
Ensures uniform material flow during cooling, preventing problems such as bubbles and cracks.
Especially important for plastic molds, good flow channel design can reduce the risk of defects during processing.
Locate Boss:
Plate:
A boss structure is provided at the bottom of the mold to secure and clamp the workpiece, ensuring stability during the molding process.
This improves the mold's clamping performance during the injection or compression molding process.
Other Auxiliary Components:
Depending on the specific design requirements, auxiliary components such as guide plates and locating pins may also be included to enhance the mold's flexibility and adaptability.
Design and Use Steps for a Three-Way Valve Mold
Determine the Design Requirements
Clearly define the three-way valve's standard specifications, dimensions, passage diameter, length, and angle, and other technical parameters.
Determine the material type (e.g., plastic, metal) and its performance requirements (e.g., strength, temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, etc.).
Perform CAD modeling.
Use Use computer-aided design (CAD) software to accurately model the three-way valve mold's 3D structure.
Based on design parameters and functional requirements, generate a detailed mold prototype that meets manufacturing requirements.
Mold Manufacturing
Create the mold cavity based on the CAD model, and use injection molding, compression molding, and other molding processes to shape the material into the shape of the three-way valve.
Part the mold (upper and lower molds) and calibrate them to ensure dimensional consistency and positional accuracy.
Mold Inspection and Repair
Perform mold dimensional inspection to ensure that all dimensions meet design requirements.
Check the mold's geometric accuracy and surface quality, repairing any areas with significant wear or defects as necessary. Repair or replace.
Trial Production and Verification
Use the pre-fabricated mold to conduct a small-batch production run, producing a three-way valve prototype and conducting performance testing.
Based on the test results, adjust mold design and process parameters to optimize mold performance and manufacturing efficiency.
Mass Production Preparation
Perform a comprehensive mold inspection to ensure all components are functioning properly and are free of defects.
Prepare the necessary production tools, equipment, and process parameters to begin mass production.
Quality Control and Continuous Improvement
During mass production, perform rigorous testing on the appearance, dimensions, and sealing performance of the three-way valve.
Based on test data and user feedback, continuously optimize mold design and process technology to improve product reliability and marketability. Market competitiveness.
Applications of three-way valve molds
Medical device manufacturing:
Used in the production of three-way valves in intravenous infusion systems, ensuring one-way flow and preventing backflow.
Highly customized product designs meet the needs of different medical institutions and patients.
Industrial fluid control:
Three-way valves are used in oil extraction, chemical processing, pipeline transportation, and other fields to regulate fluid flow and pressure.
They are commonly found in complex industrial automation equipment such as hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Laboratory and educational equipment:
Three-way valves used in educational instruments facilitate demonstration and control of experimental procedures.
They must meet safety standards and exhibit reliability and durability.
Custom Manufacturing:
We design and manufacture three-way valves with custom specifications based on customer needs to meet the unique requirements of specific industries.
We are suitable for medical equipment, industrial equipment, gift manufacturing, and other fields.
Three-way Valve Mold Maintenance and Care
Regular Cleaning
Clean the mold surface to remove dust, impurities, and other potential influencing factors to ensure that foreign matter does not enter the mold during processing.
Lubrication and Maintenance
Properly lubricate the mold to reduce friction and extend mold life. Common lubrication methods for injection molds include grease application and lubricant. Injection.
Replace damaged parts
Inspect all mold parts for wear, deformation, or other abnormalities, and replace or repair them promptly.
For plastic molds, perform regular polishing to prevent surface buildup that affects processing performance.
Calibration and Adjustment
Regularly calibrate the mold's positioning pins and guide blocks to ensure the mold remains in place during the forming process and avoid shifting or deformation.
Heat Treatment
Some metal molds undergo heat treatment processes such as annealing and normalizing to improve their mechanical properties and enhance their strength and toughness.
Environmental Control
Ensure that molds maintain stable environmental conditions (such as temperature and humidity) during storage and use to prevent deformation or corrosion caused by environmental factors.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español