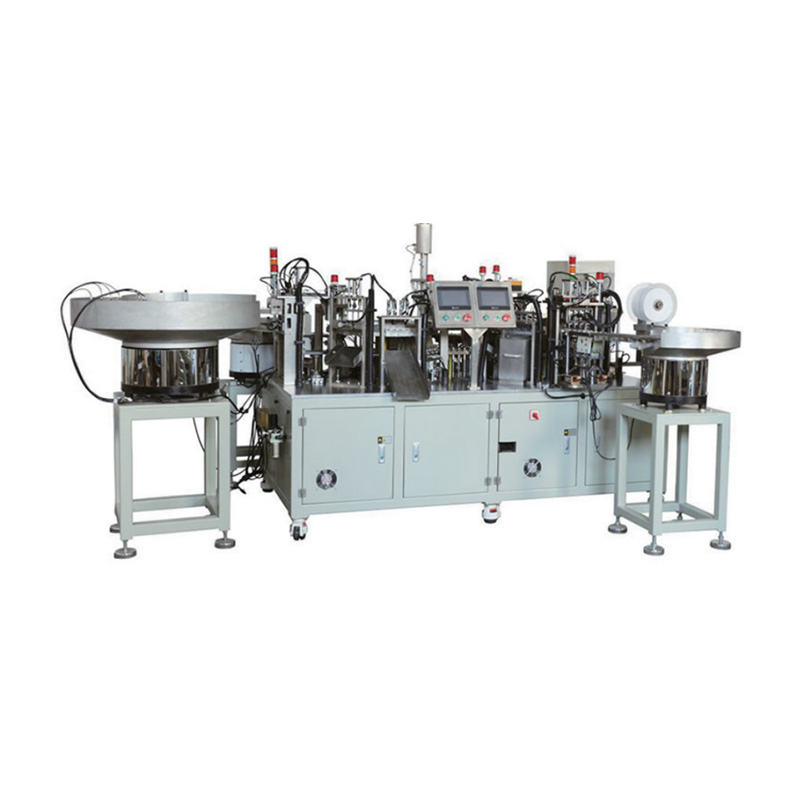
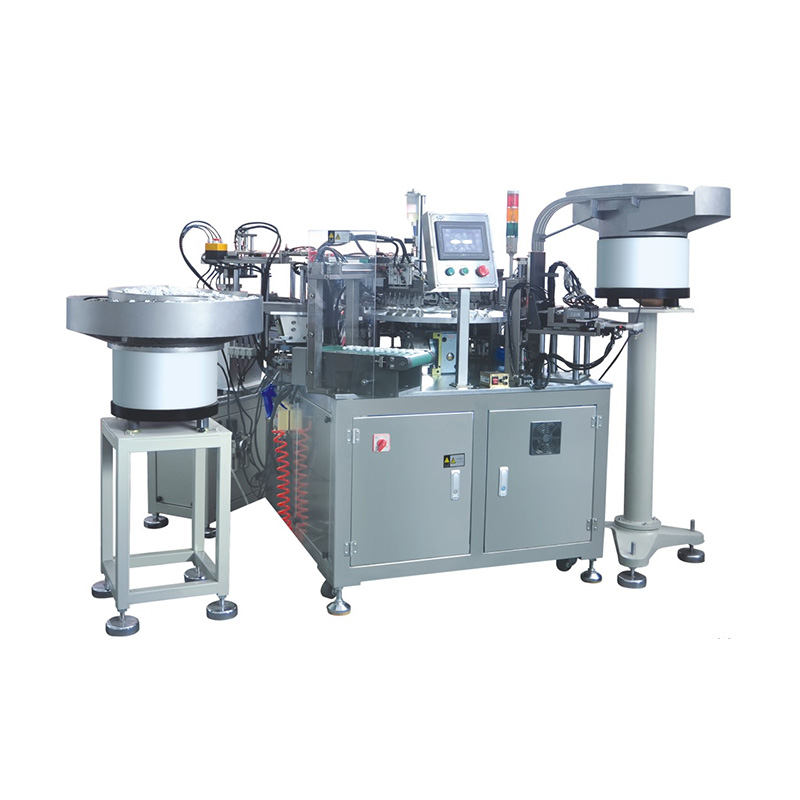
China Zhejiang Taizhou Ambe Trading Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer specializing in the production of medical equipment automation equipment.
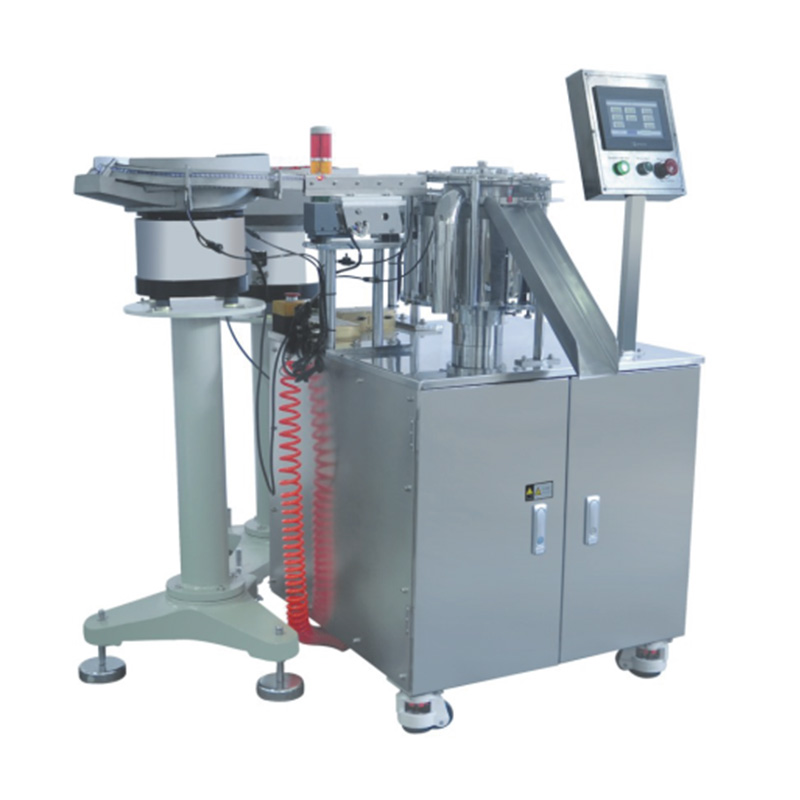
The healthcare industry is witnessing a transformative era with the advent of advanced automation technologies. Among these innovations, the syringe filling assembly machine has emerged as a game-changer, streamlining production processes while ensuring precision and safety. As pharmaceutical companies and medical device manufacturers strive to meet growing global demand, automated systems like the syringes equipment assembly machine are becoming indispensable.
The Need for Automation in Syringe Production
Syringes are among the critical medical tools, used for vaccinations, drug delivery, and diagnostic procedures. Traditional manufacturing methods, which rely heavily on manual labor, often face challenges such as contamination risks, inconsistent filling volumes, and slower production rates. The introduction of the automated syringe filler assembly machine addresses these issues by combining speed, accuracy, and sterility in a single system.
Automation not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes human error. In an industry where precision can mean the difference between life and death, the shift toward automated assembly is a logical progression.
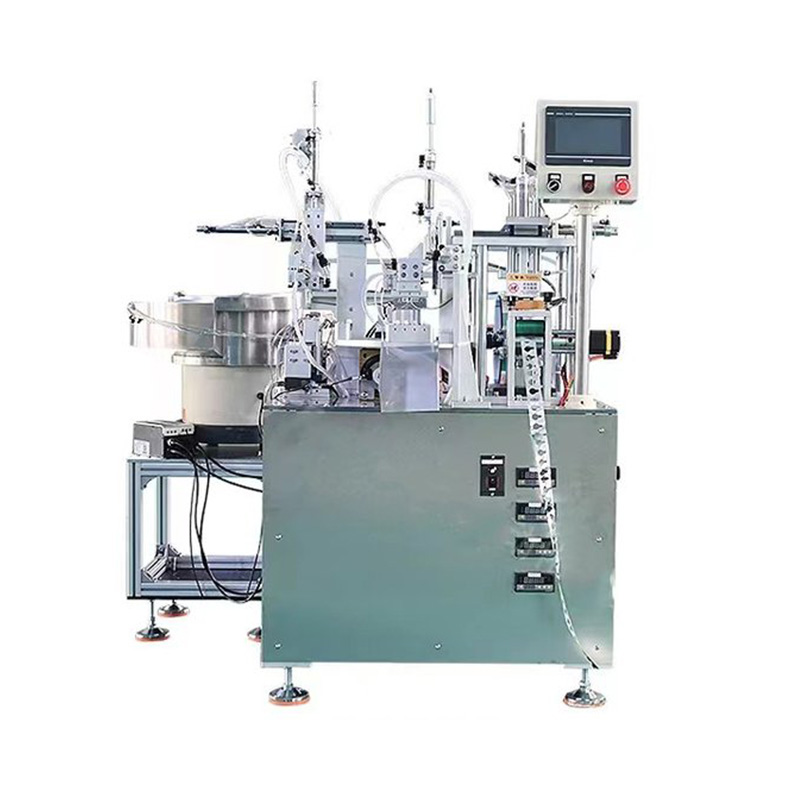
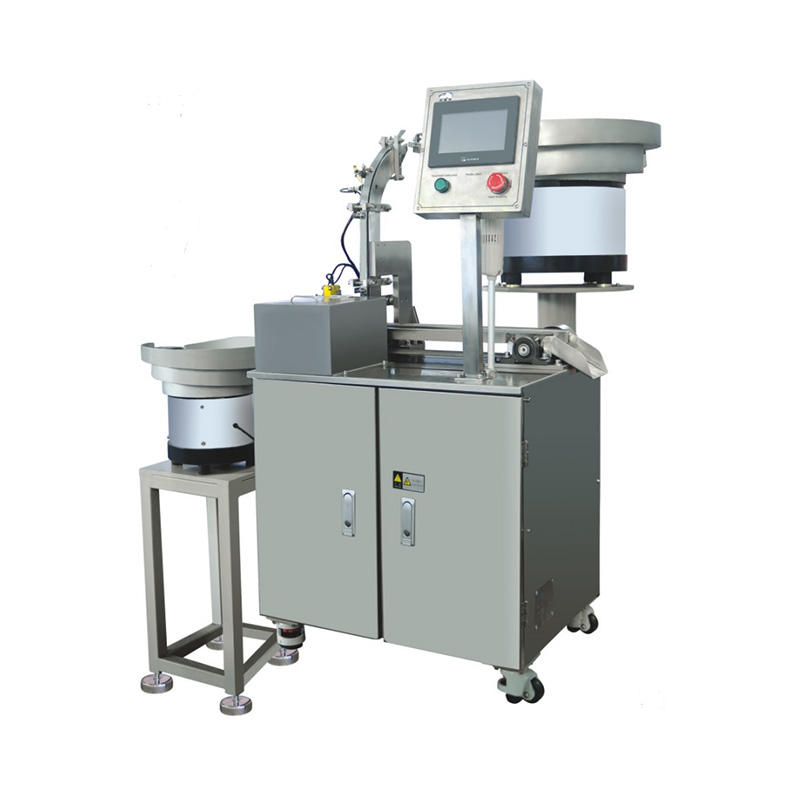
How Syringe Filling Assembly Machines Work
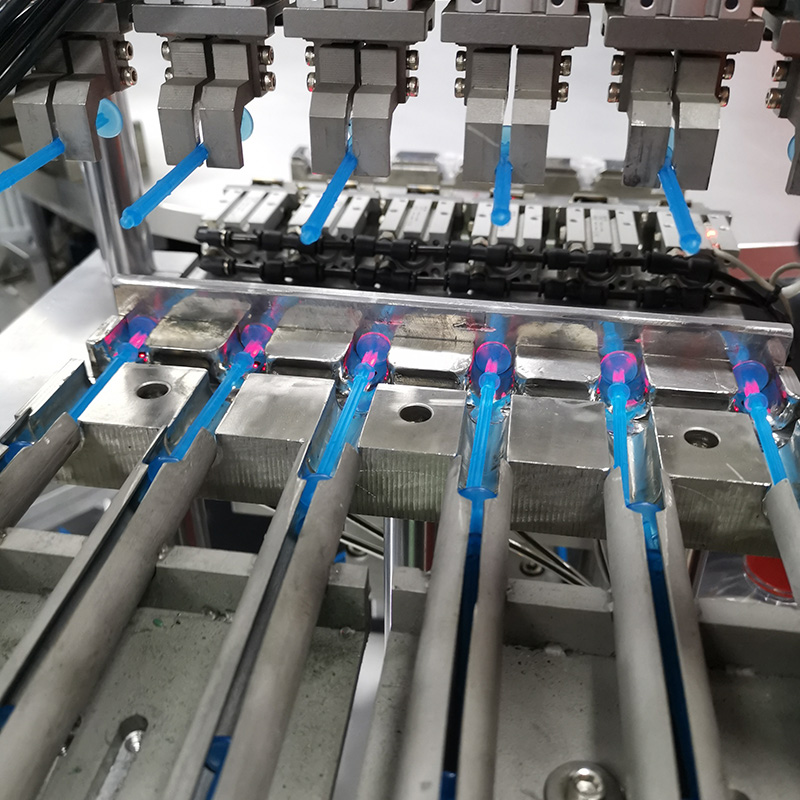
A modern syringe filling assembly machine integrates several key processes into a seamless workflow:
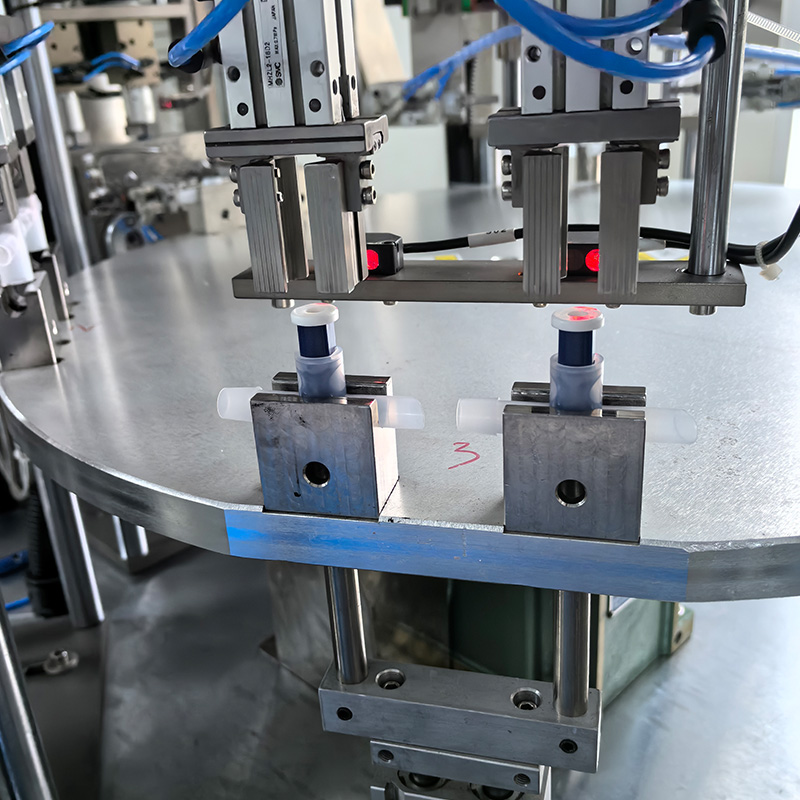
Syringe Loading – Empty syringes are fed into the machine via a conveyor system, ensuring a continuous supply without manual handling.
Precision Filling – Advanced pumps and sensors dispense exact volumes of medication or vaccines, eliminating dosage inconsistencies.
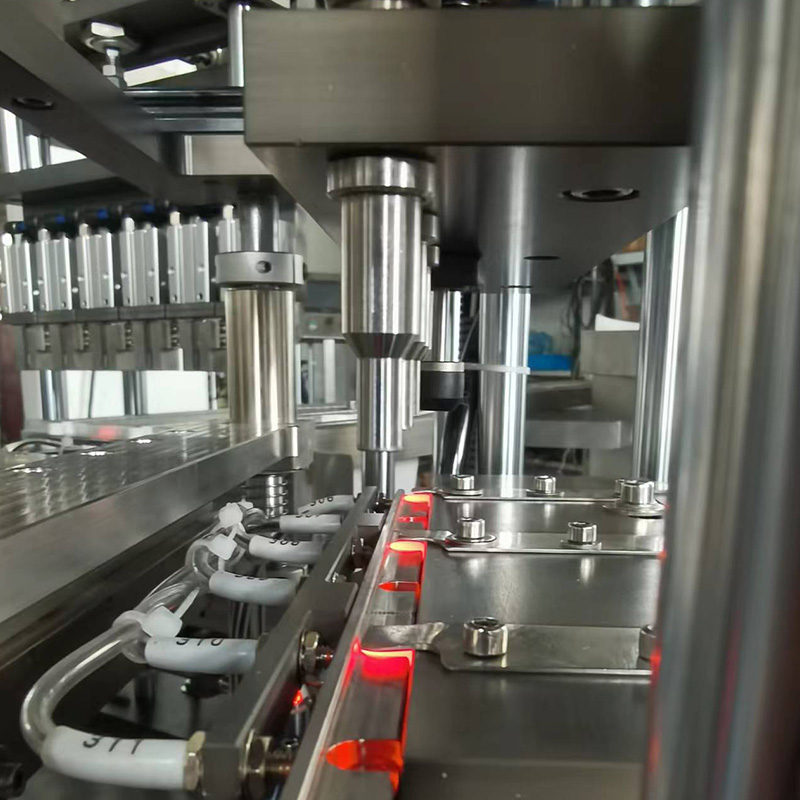
Capping and Sealing – Automated mechanisms securely cap each syringe, maintaining sterility and preventing leaks.
Inspection and Quality Control – Vision systems and sensors detect defects, ensuring only flawless syringes proceed to packaging.
The automated syringe filler assembly machine excels in high-speed production, capable of processing thousands of units per hour—far surpassing manual methods. Additionally, these machines comply with stringent regulatory standards, including FDA and ISO certifications, making them a reliable choice for pharmaceutical manufacturers.
Benefits of Automated Syringe Assembly
Enhanced Efficiency – Automation drastically reduces production time, allowing manufacturers to meet large-scale demands, such as those seen during global vaccination campaigns.
Improved Accuracy – With precise filling mechanisms, the risk of under- or over-dosing is virtually eliminated.
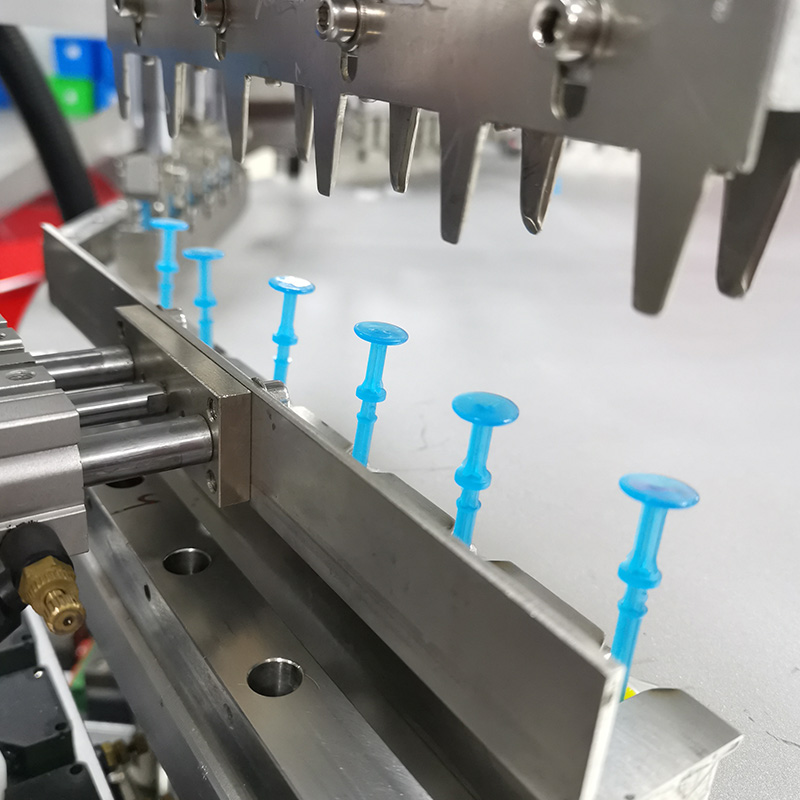

Reduced Contamination Risks – Closed systems minimize human contact, maintaining a sterile environment throughout production.
Cost-Effectiveness – While the initial investment is significant, automated systems lower long-term labor costs and reduce material wastage.
Industry Adoption and Future Trends
Leading pharmaceutical companies and contract manufacturers are increasingly integrating syringes equipment assembly machines into their production lines. The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the importance of rapid vaccine deployment, accelerating the adoption of automated filling technologies.
Looking ahead, advancements in robotics and artificial intelligence are expected to further refine these systems. Smart machines with self-learning capabilities could optimize filling processes in real-time, adapting to different viscosities and formulations without manual recalibration.
The rise of the automated syringe filler assembly machine marks a significant milestone in medical manufacturing. By combining speed, precision, and compliance, these systems are setting new benchmarks in syringe production. As technology continues to evolve, the healthcare industry can expect even greater efficiencies, ensuring that life-saving medications and vaccines reach patients faster and safer than ever before.
With automation paving the way, the future of syringe manufacturing is not just about meeting demand—it's about redefining excellence in medical care.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español